In February 2024, the Earth experienced its highest recorded temperatures, exceeding a critical threshold for global climate.
For the umpteenth month in a row, the Earth has experienced record-high temperatures. According to recent findings from Copernicus, the European Union’s agency for tracking climate change, February was the warmest month ever documented worldwide, with abnormally high temperatures both on land and in the ocean.
100-degree days and devastating wildfires.
The abnormally high temperatures are occurring while the United States is struggling with extreme weather conditions. Over the past few weeks, towns and cities throughout the country have experienced scorching hot days and destructive wildfires. ->
temperatures reminiscent of spring and summer
“Exceptionally heavy precipitation and inundation due to excessive rainfall”massive snowfall severe and suppressed violates
, and severe weather patterns that led to extreme and hindered violations in Texas.largest-ever wildfire
As planetary temperatures continue to rise due to the effects of climate change, we can expect increasingly frequent and extreme occurrences like the one that recently made history in the U.S. This trend highlights the impact of climate change and the potential for even more extreme events in the future.
C3S/ECMWF
Copernicus afirmou que a temperatura média global da superfície do ar em fevereiro foi de 13,54 graus Celsius (aproximadamente 56,4 graus Fahrenheit). Isso representa um aumento de 1,77 graus Celsius em relação à média pré-industrial para fevereiro, tornando-se o nono mês consecutivo em que cada mês foi o mais quente já registrado globalmente. Essa informação vem após
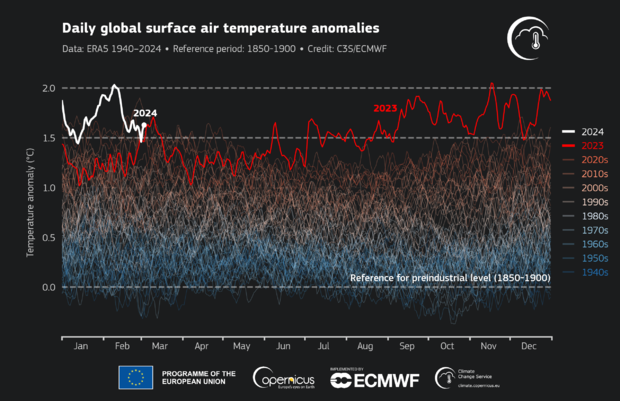
According to Copernicus, the average global surface air temperature in February was 13.54 degrees Celsius (approximately 56.4 degrees Fahrenheit). This represents an increase of 1.77 degrees Celsius from the pre-industrial average for February, making it the ninth consecutive month of record-breaking global temperatures. This information comes after 2023 broke the record for the warmest year.
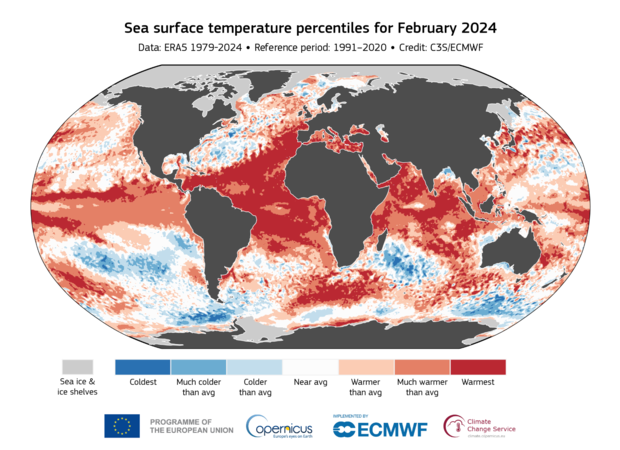
In February, the average global sea surface temperature was 21.06 degrees Celsius which is the highest recorded temperature for any month in the dataset, according to Copernicus’ findings.
increased global warming.
The elevated temperatures of the sea contribute to the process of worldwide warming. As oceans warm, they exacerbate the effects of global warming.melting sea ice
The ice’s importance lies in its ability to deflect sunlight and regulate cooler temperatures. In its absence, sea levels climb and temperatures rise, contributing to severe weather phenomena.
bacterial growth
Rising water temperatures can also result in a widespread increase in bacteria. coral bleaching
This poses a continued risk to both marine ecosystems and economies.
Many years ago, experts in climate studies cautioned about multiple triggers in climate that endanger global populations, especially those residing in coastal and island regions, with extreme weather events. These triggers consist of surpassing a span of time where global temperatures are 1.5 degrees Celsius higher than pre-industrial norms, or reaching an alarming increase of 2 degrees in temperature. The start of the calendar year was a critical milestone in this regard.
Initial occurrence documented. that global average temperatures reached the 1.5 degree warming threshold over a 12-month period.
Even though February has reached those markers, it does not necessarily mean that the entire world has reached the point of no return. However, it does suggest that human actions are still heading towards reaching that point.
The director of the Copernicus Climate Change Service, Carlo Buontempo, expressed that the data is noteworthy, but not unexpected given the ongoing warming of the climate system, which naturally results in higher temperature extremes.
Gases and UV light”
“The weather reacts to the current levels of gases and UV radiation.”greenhouse gases
“He explained that without controlling atmospheric levels of certain substances, our planet will continue to see rising average temperatures and their resulting effects in the future.
ongoing
“The most recent records are part of an ongoing trend.” :
An El Niño occurrence: that started last summer. The system occurs every two to seven years when the Pacific Ocean experiences “warmer-than-average
“The temperatures at the earth’s surface. The latest El Niño reached its highest point in December, and the World Meteorological Organization reported it as one of the top five most powerful on record.”
According to spokesperson Clare Nullis of the WMO, the phenomenon is currently experiencing a gradual decrease in intensity. However, it is expected to have lasting effects on the world’s climate in the following months. Nullis stated at a recent briefing that even after it dissipates entirely, the repercussions will still be felt.
According to her, this specific El Niño was partly caused by humans’ actions, as they persist in burning fossil fuels, which emit greenhouse gases that act as a cover over the atmosphere, trapping heat from the sun.
“Although El Niño is a natural event, it occurs within a climate that has been significantly altered by human actions. This means that all El Niño and La Niña events are influenced by human influence,” stated Nullis. Nullis also predicts that temperatures will be higher than normal in the upcoming months.
More
More
Source: cbsnews.com